The Carbon Cycle
Learn about the process of the carbon cycle on Earth.
Viewing Time
10 minutes
What is the Carbon Cycle?
Carbon is an important . It is a part of all living things. Our bodies are made of carbon, our food is made of carbon and even our clothes are made of carbon.

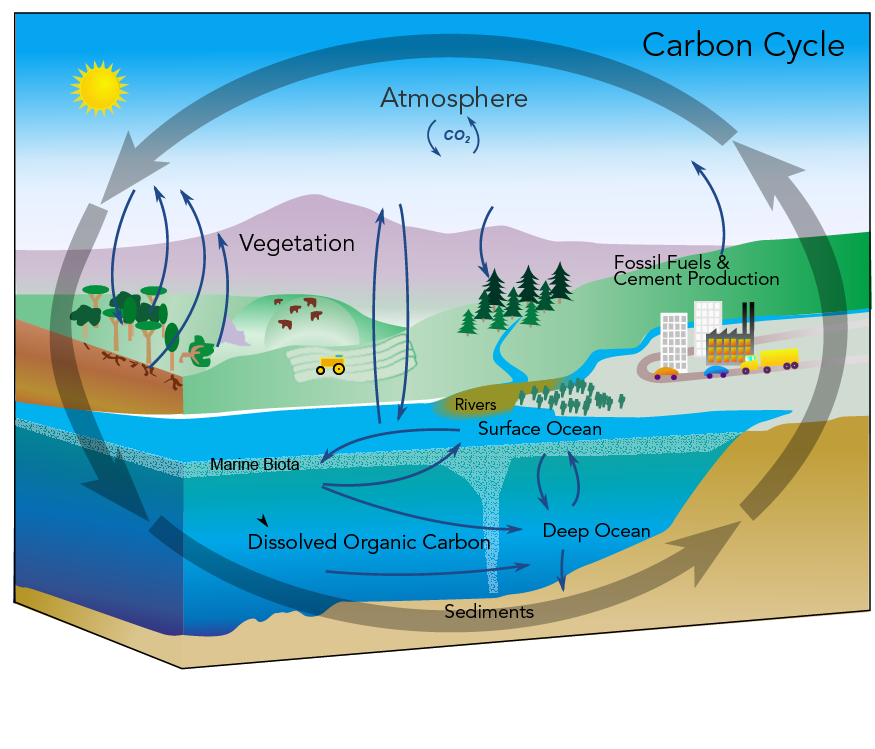
Most of Earth’s carbon is stored in rocks, which are part of the geosphere. The rest is found in oceans (hydrosphere), soils (pedosphere), living things (biosphere) and the atmosphere.
Image - Text Version
Most of Earth’s carbon is stored in rocks, which are part of the geosphere. The rest is found in oceans (hydrosphere), soils (pedosphere), living things (biosphere) and the atmosphere.
The amount of carbon on Earth stays the same. It is where you find it that changes. How carbon moves from place to place is known as the Carbon Cycle.
Click on the icons below to learn about the carbon cycle.
Did You Know?
Land plants take in about a quarter the carbon dioxide that enters the atmosphere.
Carbon takes many different forms as it cycles through the carbon cycle.
Atmospheric carbon is the term for carbon in the atmosphere.
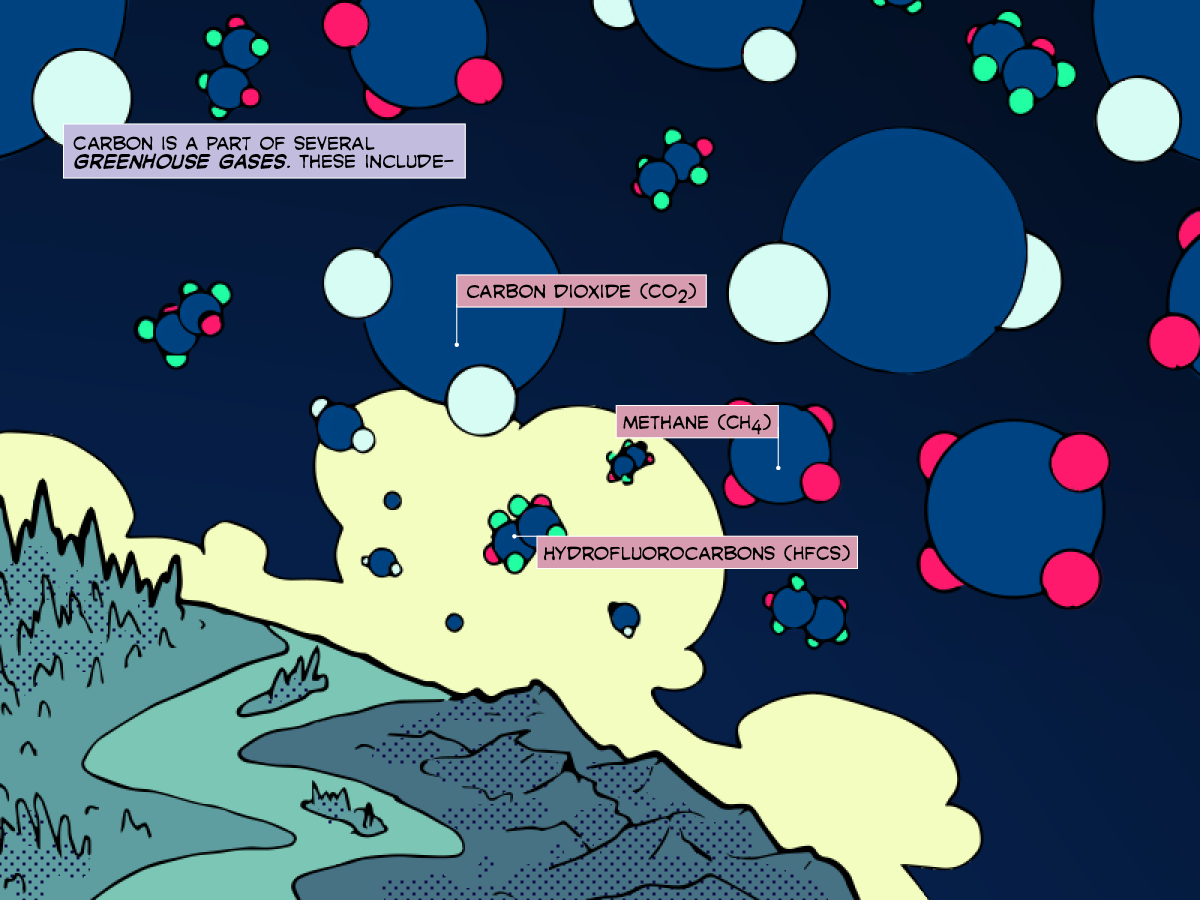
Carbon is a part of several greenhouse gases. These include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
Image - Text version
Carbon is a part of several greenhouse gases. These include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
Greenhouse gases warm the atmosphere by trapping heat in a process known as the greenhouse effect.
This warming plays an important role in climate change. Carbon dioxide is responsible for around 77 percent of the greenhouse effect.
Did You Know?
Different types of greenhouse gases trap different amounts of heat. For example, 1 kilogram of methane traps 21 times more heat than the same amount of carbon dioxide. 1 kilogram of a hydrofluorocarbon traps 1 000 times more heat than the same amount of carbon dioxide.
Carbon Sources and Sinks
Seeing how carbon flows into and out of the atmosphere helps us understand climate change. We can do this by thinking of carbon cycling between sources and sinks.
Carbon sources release carbon into the atmosphere.
Carbon sinks remove carbon from the atmosphere.
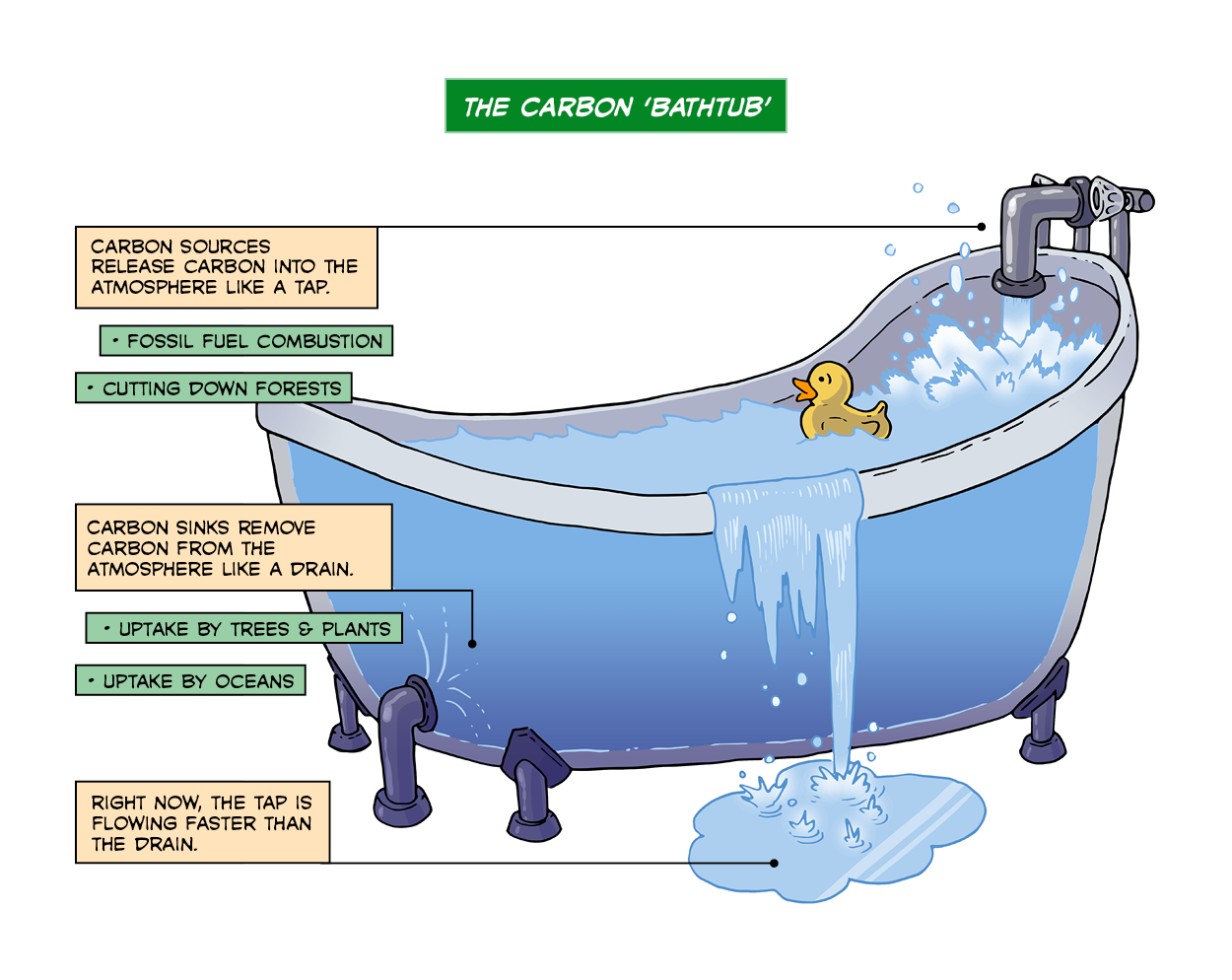
Carbon sources release carbon into the atmosphere like a tap. This includes the burning of fossil fuels and the cutting of forests.
Carbon sinks remove carbon from the atmosphere like a drain. This includes absorption by plants on land and in the oceans.
Right now, water from the tap is flowing faster than water from the drain.
Image - Text Version
Carbon sources release carbon into the atmosphere like a tap. This includes the burning of fossil fuels and the cutting of forests.
Carbon sinks remove carbon from the atmosphere like a drain. This includes absorption by plants on land and in the oceans.
Right now, water from the tap is flowing faster than water from the drain.
Before flipping each card over, guess if the picture shows a carbon source or sink. Then, flip the card to check your answer. Hint: You may want to review the picture of the carbon cycle first.

A tree is a carbon sink. Trees absorb carbon from the atmosphere through photosynthesis.

Cows are carbon sources. Animals release carbon into the atmosphere through respiration.

Ice sheets are carbon sources when they melt. They release carbon that was captured in the ice as bubbles.

Algae is a carbon sink. Algae take in carbon from the atmosphere through photosynthesis.

Driving a truck is a carbon source. Most trucks burn fossil fuels which release carbon into the atmosphere.

Soil is a carbon sink. When plants die and decompose, much of their carbon is stored in the soil.

Petroleum is a carbon sink. Fossil fuels, such as petroleum, store carbon that was removed from the atmosphere by plants.

Natural gas is a carbon source. Burning fossil fuels, such as natural gas, releases stored carbon into the atmosphere.
Misconception Alert
Fossil fuels store carbon when they remain undisturbed underground. Fossil fuels become a carbon source when they are extracted from the ground and burned. Of the total carbon released worldwide, 6 billion tons are due to fossil fuel use. 0.5 to 3.0 billion tons are due to the burning of other plant material (Hoeller, Dean, & Nicolaisen, 1991).
Carbon is always being exchanged between sources and sinks.
For thousands of years, the balance between sources and sinks kept the Earth at a temperature that was ideal for living things.
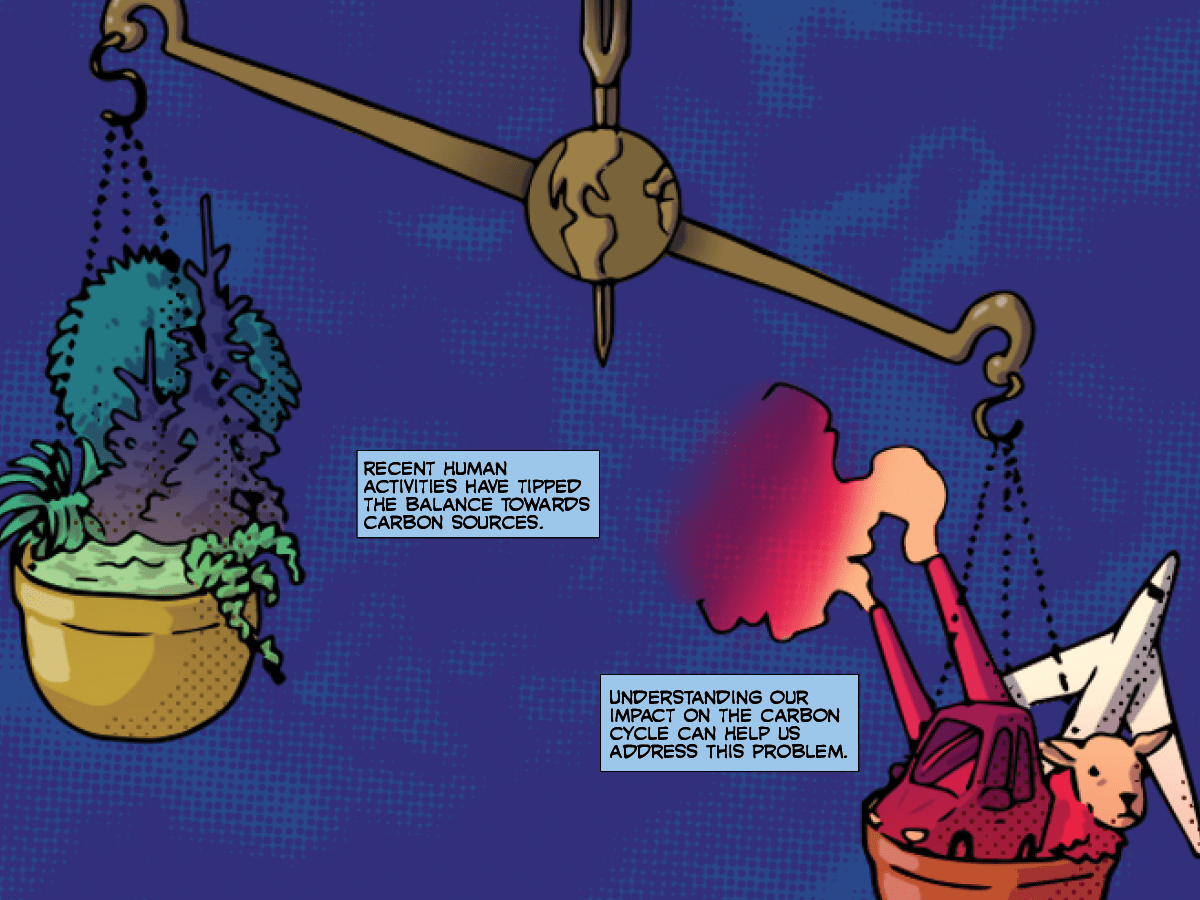
Recent human activities have tipped the carbon balance on Earth towards carbon sources.
Understanding our impact on the carbon cycle can help us address this problem.
Image - Text Version
Recent human activities have tipped the carbon balance on Earth towards carbon sources.
Understanding our impact on the carbon cycle can help us address this problem.
Check Your Understanding
Let us know what you think...
Learn More
References
Hoeller, Peter & Dean, Andrew & Nicolaisen, Jon. (1991). Macroeconomic implications of reducing greenhouse gas emissions: a survey of empirical studies. OECD Economic Studies. 16.
Ravi Jain Ph.D., P.E., ... M. Diana Webb M.L.A., in Handbook of Environmental Engineering Assessment, 2012.