Introduction to Cryptocurrency

Bitcoin logo and motherboard (adventtr, iStockphoto)

Bitcoin logo and motherboard (adventtr, iStockphoto)
Learn about cryptocurrency and how it came to be.
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital currency in which transactions are checked, and the ledger is shared, through a decentralized system. The transactions and ledger are kept secure using cryptography, rather than by a centralized authority like a bank. Cryptography is a way of protecting information using mathematics.
Some cryptocurrencies you may have heard of include:
- Bitcoin
- Ethereum
- Tether
- BNB
- DogeCoin
What is Cryptocurrency? (2019) by the International Monetary Fund (2:04 min.).
What is a decentralized digital money system?
Usually, when we think of who keeps track of our money, we think of banks. A bank is an example of a centralized approach to dealing with money. The bank is the central hub of the transactions of many different people.
Banks also work with other services, such as credit card companies, to let you borrow money for a short period. Banks can also help you to send electronic money transfers (e-transfers) to other people.
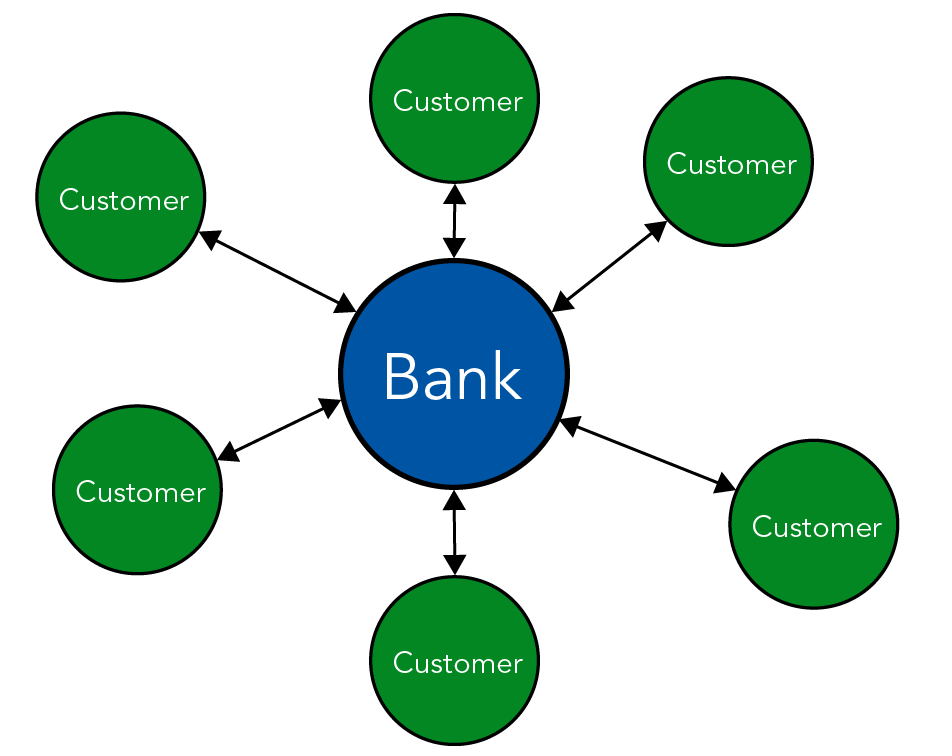
Centralized bank (©2023 Let’s Talk Science).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour diagram illustrating a centralized bank's relationships with its customers.
A large blue circle in the centre of the image is labelled, "Bank." Around this, six smaller green circles are labelled, "Customer." Each customer is connected by a double-ended, black arrow to the bank.
But what if the system was decentralized? What if everyone who used the system could be a part of keeping the ledger safe and making sure the information in it is accurate? There would no longer be the need for a bank or similar organization to be in the middle. Without a central organization, money could move more quickly. It could also move to people without access to traditional banks. Cryptocurrency works in a decentralized system.
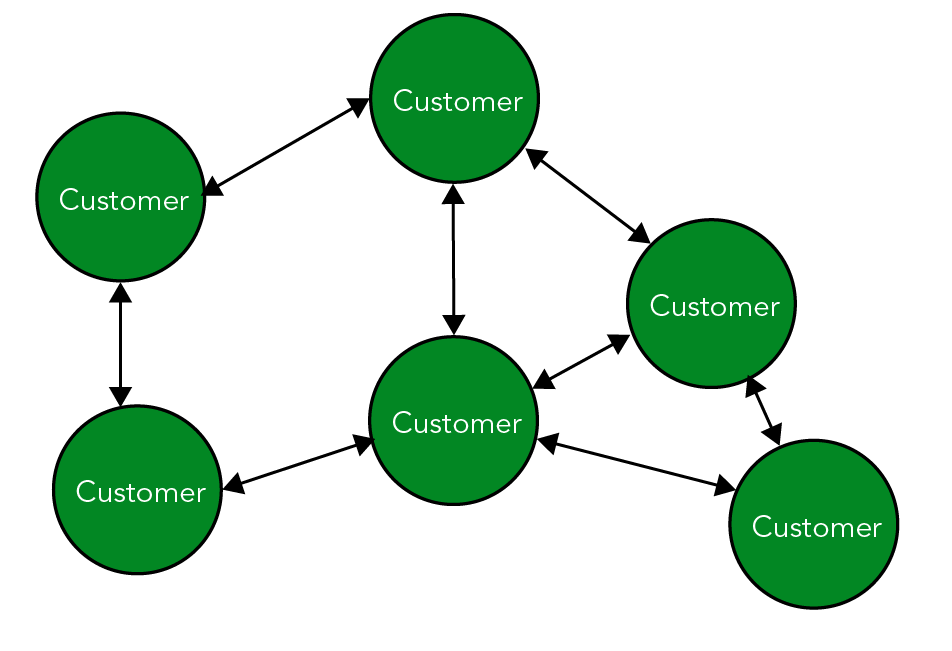
Decentralized money transfer (©2023 Let’s Talk Science).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour diagram illustrating customers' relationships in a decentralized banking system.
Six green circles labelled "Customer" in white letters, are arranged haphazardly on a white background. Small black, double-ended arrows connect each customer to two or three others.
One of the key problems with this type of decentralized system is double spending. In a traditional central bank, there is one true source of information - the ledger. For example, say you had 10 dollars in your bank account. You cannot then give 10 dollars to one friend and 10 dollars to another friend. The ledger knows that you only have 10 dollars and not 20 dollars. As long as the record is accurate, you will not be able to spend the money twice. In a decentralized system, there needs to be a way for people not to spend the same digital money more than once.
Another problem is security. Banks are very sturdy buildings with thick walls and heavy doors. Banks even have secure vaults where money and valuables such as gold bars or diamonds can be stored. Bank robbers have to really work at it to steal from banks. In the digital age, networks of all kinds are at risk of being hacked. If people are able to get at your personal information, they may be able to steal your money online.
So how did cryptocurrency attempt to overcome these problems?
The History of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency, as we know it today, came into being on October 31, 2008 with Bitcoin.
Bitcoin was the first peer-to-peer version of electronic money. It allowed payments to go from one person to another without having to go through a bank.

Various types of cryptocurrencies represented as physical coins (Source: jpgfactory via iStockphoto).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour photograph of a small pile of coins with different logos.
The coins are made from silver or gold coloured metals embossed with various designs. One has a world map and the word "ripple." Another has a large letter L, and images of computer chips and mining tools. A third is black with a gold diamond-shaped logo and the word "ethereum." Another is gold with a capital letter B, with two vertical lines added so it resembles a dollar sign.
Other coins underneath are not fully visible. They are all piled on a plain black background.
Misconception Alert!
Bitcoins are not coins! They, and other cryptocurrencies, exist in digital form only. Some people have printed Bitcoins and other coins as fun, collectible items but these cannot be used as currency.
Bitcoin also solved the problem of double spending using a decentralized ledger. Anyone in the Bitcoin network can access the ledger to check that the right amount of currency was sent and received.
Finally, it is almost impossible to change information in the ledger because the information is encrypted using cryptography. To learn more about how the Bitcoin system works, check out our Backgrounder: Introduction to Blockchain.
Did you know?
Like other types of currencies, Bitcoin is divisible. The smallest unit of Bitcoin is the Satoshi. This name comes from the person who dreamed up the Bitcoin system - Satoshi Nakamoto. One Satoshi is worth 0.00000001 Bitcoins (BTC).
Not only is Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies used for online transactions, they have value compared to standard national currencies. This value is determined by the concept of supply and demand. When demand for Bitcoin increases, so does its value.
Try this!
You can find out how much one Bitcoin is worth in your country by doing an online search for “How much is one Bitcoin worth in x dollars?”
How do you get Bitcoin?
Unlike real money, which governments can decide to make more of, there is a limited supply of Bitcoin. The creators of Bitcoin set it up to resemble the finite supply of a precious metal such as gold. Just like precious metals, Bitcoin can be mined.
Bitcoin “mining” is not the same as mining precious metals. Bitcoin miners use very powerful computers to use cryptography on the data. If a Bitcoin miner is the first to be successful, they receive Bitcoin as a reward.
What is Bitcoin Mining (2017) by The Federalists Society (2:39 min)
Remember how cryptocurrency exists in a decentralized system? The equations solved by Bitcoin miners help to check the legitimacy of other Bitcoin transactions and prevent other people from double spending. It is kind of like when you check someone else’s homework!
Since the creators of Bitcoin wanted this cryptocurrency to resemble a precious metal, there are only 21 million Bitcoins that can ever be mined. Other cryptocurrencies do not have this kind of limited supply, but limit the number of coins that can be mined or added each day.
Did you know?
New Bitcoins are added to the Bitcoin supply approximately every 10 minutes and 19 million have already been mined.
What can you do with Cryptocurrency?
Just like with precious metals, once Bitcoin or other cryptocurrency has been mined, it can be bought and sold to other people. You can buy cryptocurrency at a cryptocurrency exchange such as Coinbase, Gemini or even Paypal using regular money.
For many people, cryptocurrency is an investment. Just like other currencies the value goes up and down, people buy cryptocurrencies with the hope that the value will go up and they can sell it for more money later on.
It is also possible to buy things with Bitcoin. Most retailers still do not accept Bitcoin as currency but here is a list of some places that do!
The Downsides of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency sounds pretty good, but there are some downsides.
- Cryptocurrency is not not guaranteed by the government
If something terrible happens to a bank, the government can step in to help out. And if something strange happens, like your bank account being hacked, your bank will help you sort it out. These safeguards are not available for cryptocurrency. - Cryptocurrency is not a legal form of money (in most places)
As of May 2022, El Salvador and the Central African Republic were the only countries in the world to consider Bitcoin to be legally acceptable money. In the rest of the world, rules around cryptocurrency vary by country. - Cryptocurrency accounts can still be hacked
Just like with any online service you use, it is possible for hackers to get into your account and pretend to be you. When this happens, hackers can give your money to someone else (like themselves!). - Cryptocurrency transactions can be slow
Since transactions using cryptocurrency must be checked and added to the Blockchain, it can take up to hours for transactions to clear. Bitcoin’s network can only process up to 7 transactions per second and Etherum’s network can process 20 transactions per second. This is slow compared to Visa’s network that can process up to 24,000 transactions a second. - Cryptocurrency transactions need a lot of computing power
The processes used to verify transactions in the decentralized system and mine cryptocurrency require many computers. These computers use a lot of energy - sometimes as much energy as entire countries consume. Depending on the energy used to power the electricity grid for these computers, cryptocurrency can actually produce a large amount of greenhouse gas emissions.
In conclusion
Cryptocurrency is still a very new technology. It has advantages for people looking for ways to transfer money without the need of banks. On the flip side, cryptocurrency,like all money, can be stolen. It also requires a huge amount of energy that could be used for other things.
Question #1
Do you think that cryptocurrency is here to stay? Why or why not?
Learn More
What is Crypto | Cryptocurrency Explained for Kids | Crypto For Kids (2022)
This video (11:31 min.) for kids has lots of great questions and answers about cryptocurrency.
Talking About Cryptocurrency
This page from roostermoney.com offers children a balanced view of cryptocurrency that will help them gain a good footing in this very new side of financial literacy.
Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency for Beginners and Kids (2022)
In this video (4:04 min.), a boy named Kart explains the basics of Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency.
But how does bitcoin actually work?
This video (25:15 min.) from 3Blue1Brown explains in detail how Bitcoin works. The video covers topics such as decentralization, double spending, ledgers and the blockchain.
References
CNBCTV18 (Apr 18, 2022). What Is A Physical Bitcoin, And What Is It Worth?
Corporate Finance Institute (n.d.). Introduction to Cryptocurrency.
Crypto.com (Jan 3, 2020). A Deep Dive Into Blockchain Scalability.
George, K. (Nov 30, 2022). Cryptocurrency Regulations Around The World. Investopedia.
Hong, E. (May 5, 2022). How Does Bitcoin Mining Work? Investopedia.
Kiddle (n.d.). Blockchain Facts For Kids.
Nakamoto, S. (n.d.). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. Bitcoin.org.
River Financial (n.d.). How Is The Bitcoin Price Determined?
Zhang, Y. (2021). Blockchain Viewed From Mathematics. Notices From The American Mathematical Society 68 (10): 1740-1751
Zoldan, A. (n.d.). Still Confused About Blockchain? Use This Explanation Even a 6-Year-Old Can Understand. Inc.