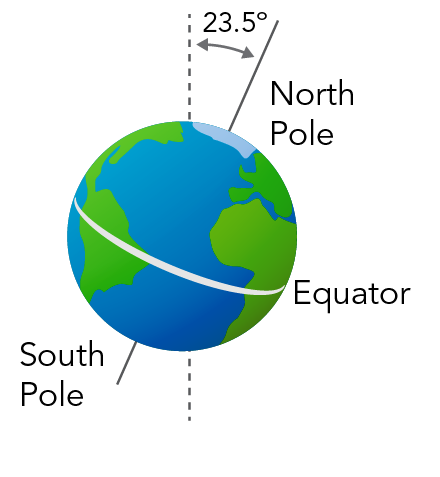
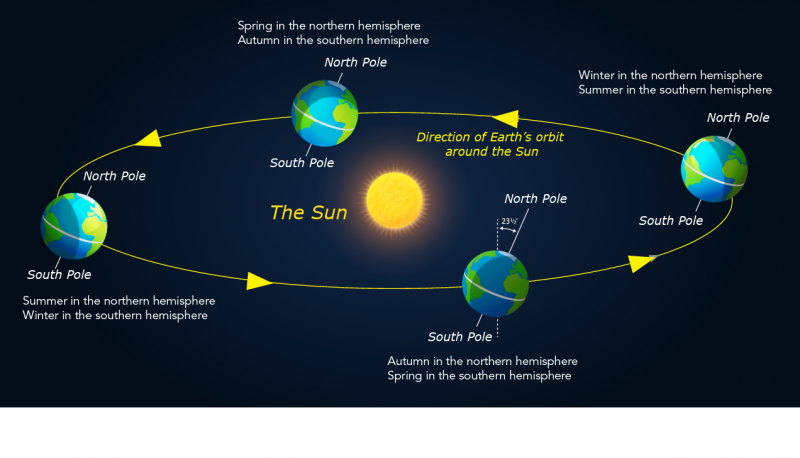
Why do we have seasons?
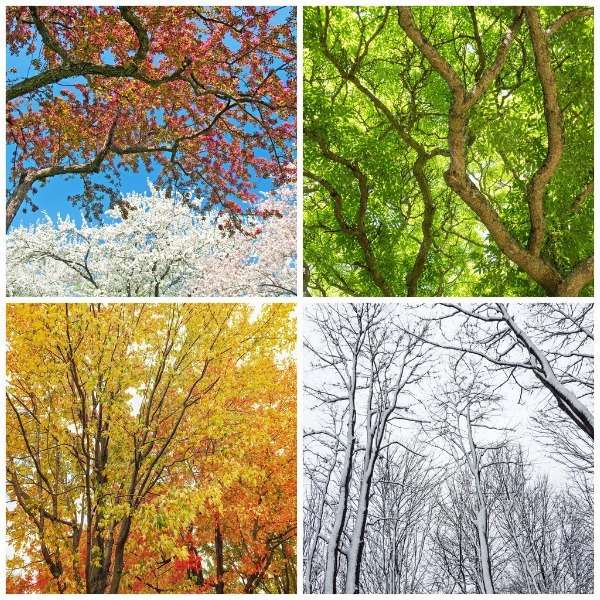

Tree through the four seasons (Studio Light and Shade, iStockphoto)

Tree through the four seasons (Studio Light and Shade, iStockphoto)
4.7
How does this align with my curriculum?
BC
1
Science Grade 1 (June 2016)
Big Idea: Observable patterns and cycles occur in the local sky and landscape.
NU
1
K-6 Science and Technology Curriculum (NWT, 2004)
Earth and Space Systems: Daily and Seasonal Cycles
YT
1
Science Grade 1 (British Columbia, June 2016)
Big Idea: Observable patterns and cycles occur in the local sky and landscape.
NT
1
K-6 Science and Technology Curriculum (NWT, 2004)
Earth and Space Systems: Daily and Seasonal Cycles
AB
5
Science 5 (2023)
Earth Systems: Understandings of the living world, Earth, and space are deepened by investigating natural systems and their interactions.
AB
1
Science 1 (2023)
Earth Systems: Understandings of the living world, Earth, and space are deepened by investigating natural systems and their interactions.