How do alkaloids cause addiction?

Field of tobacco plants, which are a source of nicotine (2windspa, iStockphoto)

Field of tobacco plants, which are a source of nicotine (2windspa, iStockphoto)
How does this align with my curriculum?
| Grade | Course | Topic |
|---|
Alkaloids are found in some of the most addictive substances that humans consume. What are alkaloids, and how do they cause addiction?
What do nicotine, codeine, morphine, caffeine, and diamorphine (better known as heroin) all have in common? If you said they’re all addictive substances, you’re right. Specifically, these addictive substances belong to a group of molecules called alkaloids.
What are alkaloids?
Alkaloids are naturally-occurring compounds that occur in some groups of plants. More than 3 000 different types of alkaloids have been identified in plants. Morphine and codeine are derived from a substance found in the seed capsules of the opium poppy (Papaver somniferum).

Nicotine, also an alkaloid, is found in plants in the nightshade family like cauliflower, tomatoes, eggplants, potatoes and tobacco.
Did you know?
You would have to eat about 350 large tomatoes to ingest as much nicotine as you would sitting next to a chain-smoker for three hours.
Scientists aren't entirely sure why some plants produce alkaloids. It may be linked to a plant's seed development process. Scientists also think that alkaloids might protect plants against insects that eat them. It could be like a plants’ warning call saying “Hey, get away from here, leave my leaves alone!” The alkaloids the plants produce usually have an effect on an insect’s nervous system. Also, they often make the plant taste bad so that insects will learn to avoid them.
What is the chemical structure of alkaloids?
Alkaloids are a diverse group of chemical compounds. Compounds are substances formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together. Scientists classify compounds by the groups that create them. Alkaloid compounds contain an amine group. An amine group contains a nitrogen atom and a lone pair of electrons.

In general, an alkaloid is made up of:
- an amine group;
- one or more carbon atoms; and
- multiple hydrogen atoms (H).
How does the chemical structure of alkaloids vary?
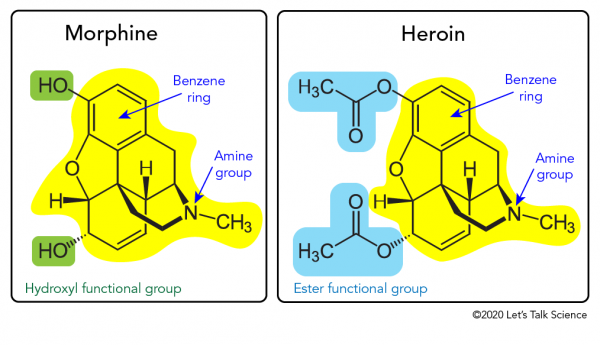
Let’s compare the structure of two alkaloids — morphine and heroin. Morphine is a strong prescription drug that many doctors prescribe as a painkiller. Heroin is a strong non-prescription drug that is illegal in Canada. Both morphine and heroin are narcotics, which are now more formally called opioids.
Did you know?
Heroin was first sold as a cough suppressant and a substitute for morphine.
Morphine and heroin have a similar chemical structure. Both have a benzene ring and an amine group. However, the structures of each of the compounds have different functional groups. These are groups of atoms within a molecule that give the compound its unique characteristics. Chemists use functional groups to classify different compounds. For example, morphine and heroin differ by two functional groups. Morphine has two alcohol, or hydroxyl, functional groups (-OH). Heroin, on the other hand, contains two ester functional groups (-OCOCH3) in place of morphine’s two hydroxyl groups.
How do alkaloids affect humans?
We know that alkaloids affect insects, but how do they affect people? Some alkaloids, like morphine and codeine, are taken because they relieve pain, but they can also make people feel sleepy. Nicotine can make people feel calm, relaxed and even euphoric. Why the difference?
Human brains have reward pathways. Everyday actions, such as eating a piece of chocolate or drinking a glass of water when you’re very thirsty, can trigger the reward pathways in your brain. However, other things can also trigger these reward pathways, like alkaloids.
Let's look at morphine. When a patient is given morphine, it binds to opioid receptors in the body’s neurons. This reduces the pain signal that is sent to the brain. It also activates the reward system and likely increases the production of endorphins, which are like the body’s own opiate. Endorphins are produced in response to activities such as creative pursuits, exercise and social activities.
Did you know?
The first reference to opium as a feel-good substance may be as early as 3 400 BCE! In fact, ancient Sumerians called it the “joy plant.”
Morphine also releases a chemical called dopamine in the brain. It was once thought that dopamine was responsible for the feelings of euphoria (the “high”). But now scientists think dopamine may actually be responsible for getting us to repeat pleasurable activities.
How do people get addicted to alkaloids?
When a person takes an addictive drug over time, that person may develop a tolerance for it. You can think about this process like a push-up exercise challenge. On the first day, you can only do one push-up. If you keep practicing every day, after 20 days, you can probably do many more push-ups. That one push-up you did on day one will seem easy.
Let’s imagine a similar process with a person taking morphine. After a person has taken morphine many times, it’s harder for the body to produce endorphins. Also, it will be harder for the body’s reward pathways to produce dopamine without a little boost of morphine. As a result, a person may feel that they need morphine to feel “okay.” Over time, a person may need larger and larger doses of the drug, and find it very difficult to stop taking it. This is known as drug dependence. Addiction is more than just a dependence on a certain drug. It is a chronic health condition with many impacts on people, both physical and mental.
Summing up
Alkaloids have been useful to humans in our past and present. Painkillers such as codeine and morphine make life bearable for many people. And for some people, the day cannot start without a cup of coffee or cola. But as you’ve just learned, alkaloids impact the brain’s reward pathway which can make them very addictive.
If you or someone you know is struggling with addiction, speak with a medical professional.
Starting Points
- Do you drink coffee or caffeinated energy drinks? Do you think you are addicted to caffeine? Why or why not?
- Have you ever taken a drug like codeine or morphine? For what type of pain was this drug prescribed? How did it make you feel?
- What are some of the impacts on society of alkaloid addictions?
- How is the administration of alkaloid drugs managed by the medical system? (Note: this question may require some additional research.)
- What is the basic chemical structure of an alkaloid? What makes one alkaloid different from another? What are some examples of alkaloids?
- How does a narcotic or opiate drug act in the human body to reduce pain?
- Where were alkaloids originally derived? What is the role of alkaloids in plants?
- Explain the concept of drug tolerance? How might drug tolerance lead to addiction?
- How have developments in science and technology impacted on the development of opioid drugs?
- What books (fiction or nonfiction) have you read about opioid addiction? Did you empathize with the people/characters in the book? What things did you learn about addiction by reading the book?
- A Street Cat Named Bob (2016) is a movie about a young busker living on the streets in London, England who is working on breaking his narcotics addiction. Watch this movie, or read the memoir that inspired the movie, A Street Cat Named Bob: How One Man and His Cat Found Hope on the Streets by James Bowen. Discuss the different things that contributed to his eventual success at beating his heroin dependence.
- This article can be used to support teaching and learning of Biology, Chemistry, Anatomy and Health related to organic chemistry and the nervous system. Concepts introduced in this article include alkaloids, compound, amine, functional groups, reward pathway, opioid receptors, tolerance and physical dependency, etc.
- After reading this article and watching the embedded videos, teachers could have students complete a Concept Definition Web for the concept of alkaloids. Ready-to-use reproducibles using this strategy are available in [Google doc] and [PDF] formats.
- To help students obtain and summarize information presented the text and the embedded students could use a Print-Video Venn Diagram learning strategy. A ready-to-use reproducible for this article is available in [Google doc] and [PDF] formats.
- Students could explore issues surrounding opiate drugs using a Silent Discussion/Graffiti learning strategy. Ready-to-use reproducibles for this article are available in [Google doc] and [PDF] formats.
Connecting and Relating
- Do you drink coffee or caffeinated energy drinks? Do you think you are addicted to caffeine? Why or why not?
- Have you ever taken a drug like codeine or morphine? For what type of pain was this drug prescribed? How did it make you feel?
Relating Science and Technology to Society and the Environment
- What are some of the impacts on society of alkaloid addictions?
- How is the administration of alkaloid drugs managed by the medical system? (Note: this question may require some additional research.)
Exploring Concepts
- What is the basic chemical structure of an alkaloid? What makes one alkaloid different from another? What are some examples of alkaloids?
- How does a narcotic or opiate drug act in the human body to reduce pain?
- Where were alkaloids originally derived? What is the role of alkaloids in plants?
- Explain the concept of drug tolerance? How might drug tolerance lead to addiction?
Nature of Science/Nature of Technology
- How have developments in science and technology impacted on the development of opioid drugs?
Media Literacy
- What books (fiction or nonfiction) have you read about opioid addiction? Did you empathize with the people/characters in the book? What things did you learn about addiction by reading the book?
- A Street Cat Named Bob (2016) is a movie about a young busker living on the streets in London, England who is working on breaking his narcotics addiction. Watch this movie, or read the memoir that inspired the movie, A Street Cat Named Bob: How One Man and His Cat Found Hope on the Streets by James Bowen. Discuss the different things that contributed to his eventual success at beating his heroin dependence.
Teaching Suggestions
- This article can be used to support teaching and learning of Biology, Chemistry, Anatomy and Health related to organic chemistry and the nervous system. Concepts introduced in this article include alkaloids, compound, amine, functional groups, reward pathway, opioid receptors, tolerance and physical dependency, etc.
- After reading this article and watching the embedded videos, teachers could have students complete a Concept Definition Web for the concept of alkaloids. Ready-to-use reproducibles using this strategy are available in [Google doc] and [PDF] formats.
- To help students obtain and summarize information presented the text and the embedded students could use a Print-Video Venn Diagram learning strategy. A ready-to-use reproducible for this article is available in [Google doc] and [PDF] formats.
- Students could explore issues surrounding opiate drugs using a Silent Discussion/Graffiti learning strategy. Ready-to-use reproducibles for this article are available in [Google doc] and [PDF] formats.
Learn more
Five Things To Know About Heroin's Curious Chemistry History (2017)
Article from Forbes that includes some interesting facts about the history of heroin.
Why We Have Pain & How We Kill It (2013)
A video (10:04 min.) from SciShow exploring why humans experience pain, and how science helps us deal with it.
Is There Really a Difference Between Drug Addiction and Drug Dependence? (2019)
An article from Scientific American that explains the difference between a dependence and an addiction.
References
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2018, August 17). Alkaloid.
Lumen Learning. (n.d.). Amines and amides.
Mithofer, A. & Boland, W. (2012). Plant defense against herbivores: Chemical aspects, The Annual Review of Plant Biology, 63, 431-450. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103854
National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2018). Drugs, brains, and behavior: The science of addiction.
National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2019). The neurobiology of drug addiction - Definition of tolerance.
National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2019). The neurobiology of drug addiction - The reward pathway.
Purdue University. (n.d.). Amines, alkaloids, and amides.
Purdue University. (n.d.). Functional groups.