Social Emotional Learning

Two boys in school library (kali9, iStockphoto)
Learn about social-emotional learning and how to foster it in STEM learning environments.
School is a powerful place. It is an environment where students not only acquire knowledge, but also where they learn life skills and develop values that will help them grow to their fullest potential as human beings. It is also a space where students learn about themselves and ways to positively interact with others. In other words, a place where students can develop socially and emotionally.
What is social-emotional learning?
Social-emotional learning (SEL) is the process of developing the self-awareness, self-control, and interpersonal skills that are vital for school, work, and life success.
People with strong social-emotional skills are better able to cope with everyday challenges and benefit academically, professionally, and socially. From effective problem-solving to self-discipline, from impulse control to emotion management and more.
What are the dimensions of social-emotional learning?
Social-emotional learning in school can include everything from goal setting and stress management to social awareness and relationship building. SEL is not a program of studies, rather it is an approach to teaching that can be incorporated into every stage of learning, from preschool to high school.
Here are some areas of learning associated with SEL.
Self-awareness and Sense of Identity
This area of learning includes helping students to build an understanding of their own identity as well as to recognize strengths and needs.
Self-management
This area of learning includes helping students to control impulses and set goals. It also includes helping students to maintain positive motivation and perseverance.
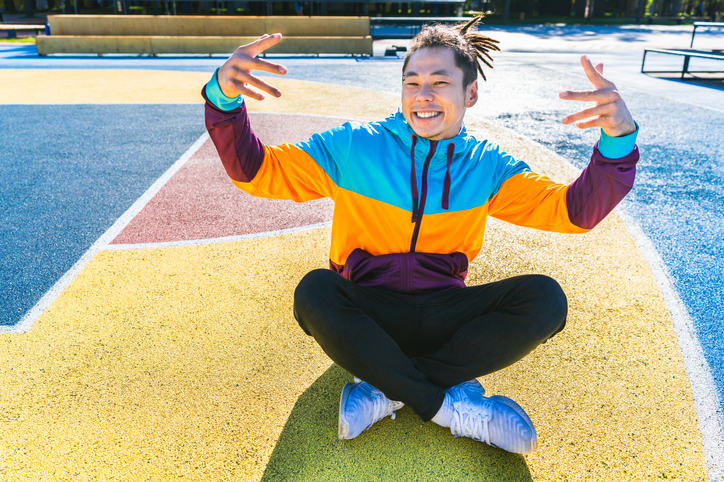

A young person breakdancing outdoors (Source: Diamond Dogs via iStockphoto).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour photograph of a young person sitting in a brightly painted playground, gesturing toward themselves.
They are smiling broadly with their arms and fingers outstretched and pointing back towards themselves. They have brown hair in a spiky ponytail, and a bright blue, yellow and maroon jacket.
Emotional Awareness
This area of learning includes helping students to identify and communicate their emotions as well as understand the emotions of others. It can also help students identify and cope with stress and other challenges.
Critical and Creative Thinking
This area of learning includes helping students to develop decision-making and problem-solving skills, including thinking about the consequences of their decisions and behaviour.
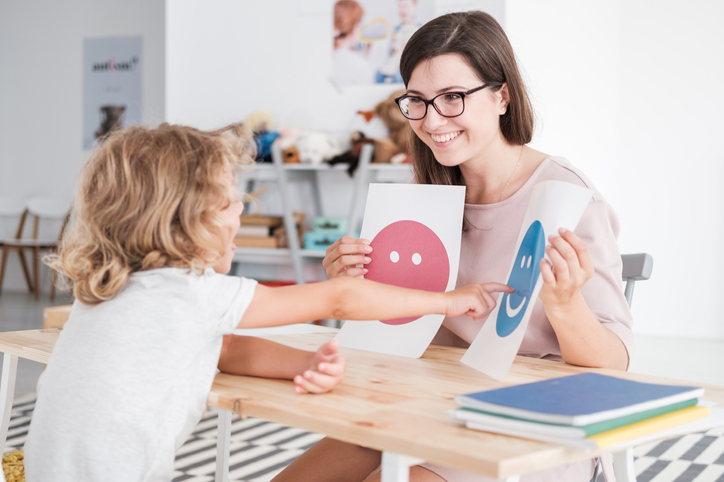

Student pointing to an image of a happy face (Source: KatarzynaBialasiewicz via iStockphoto).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour photograph of an adult sitting across the table from a child, holding pictures of a happy face and another face.
The adult is smiling at the child, whose back is to the camera. The child is reaching across the table to put one finger on the piece of paper printed with a blue happy face. The other paper has a pink face, but the child's arm is blocking its expression.
Social Awareness
This area of learning includes helping students to see things from other people’s perspectives, show empathy, and appreciate diversity.
Healthy Relationships
This area of learning includes helping students to develop communication, cooperation, and conflict resolution skills, as well as to respect different perspectives.
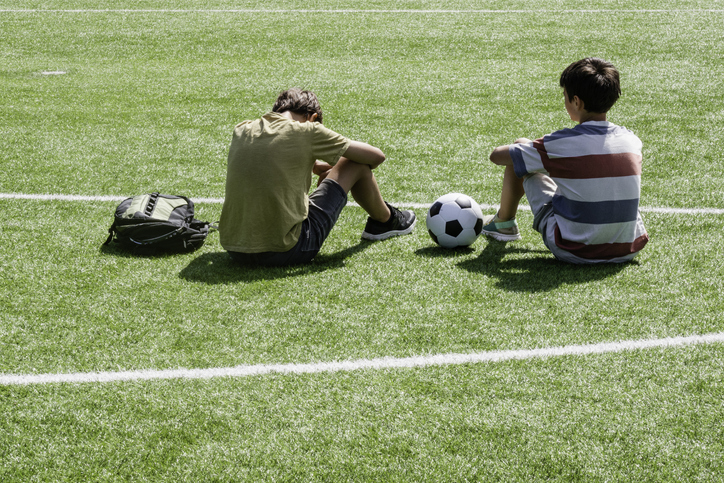

Student showing empathy to another student (Source: vejaa via iStockphoto).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour photograph of two young people sitting on a soccer field with a ball between them.
Both have their backs to the camera, sitting with their arms wrapped around their knees. The person on the left is looking down at the grass. The person on the right is looking over towards them. A soccer ball sits on the grass between them, and a backpack is over to the left.
Incorporating SEL in the STEM classroom
STEM activities provide opportunities for students to develop domains of SEL.
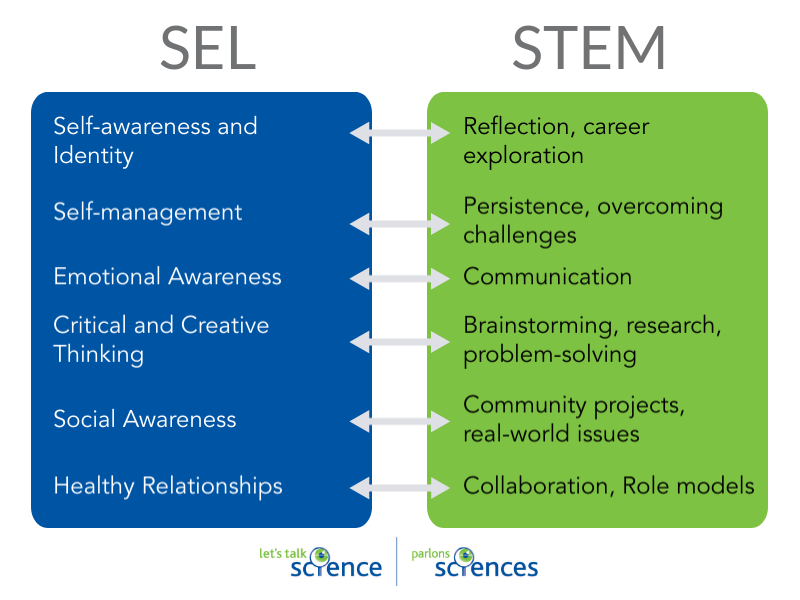
SEL and STEM (Adapted from: STEM and SEL: Important Connections for Student Development by Dr. Jacie Maslyk).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour chart with two lists of six ideas under the headings of SEL and STEM, with double-ended arrows between each one.
On the left, the SEL list is in white text on a blue rectangle. The STEM list is in black text on a green background.
Under SEL, the first item reads, "Self-awareness and Identity." The corresponding item under STEM reads, "Reflection, career exploration."
The second item under SEL reads, "Self-management." The corresponding item under STEM reads, "Persistence, overcoming challenges."
The third item under SEL reads, "Emotional awareness." The corresponding item under STEM reads, "Communication."
The fourth item under SEL reads, "Critical and creative thinking." The corresponding item under STEM reads, "Brainstorming, research, problem-solving."
The fifth item under SEL reads, "Social Awareness." The corresponding item under STEM reads, "Community projects, real-world issues."
The sixth item under SEL reads, "Healthy relationships." The corresponding item under STEM reads, "Collaborations, Role models."
Self-awareness and Identity
It is important that all students “see themselves” in STEM. This can include being exposed to people of different genders and cultures who work in STEM.
It is also important for all students to see themselves as capable learners of STEM. Teachers should actively encourage the idea that STEM is for all, and not only for certain types of students (e.g., smart kids, boys, etc.).
Try this!
Reflection is a big part of self-awareness. As often as possible, use reflection strategies such as Exit Slips and as integral parts of STEM lessons.
Students can explore the breadth and depth of STEM careers by checking out these STEM Career Profiles and 360 Videos.
Self-management
Regulating one's emotions and behaviours is key to self-management. When students work together to complete tasks, such as during group STEM activities, they must regulate their emotions and demonstrate persistence in order to be successful.
Persistence is key to many design & build activities. When students test prototypes, they are not always successful at first. Teachers should encourage students not to see this as failure, but rather as an opportunity to learn from what did not work and to apply this learning forward to revise prototypes.
Try this!
Incorporate open-ended engineering design challenges as part of STEM learning. Students could try one of these design & build activities.
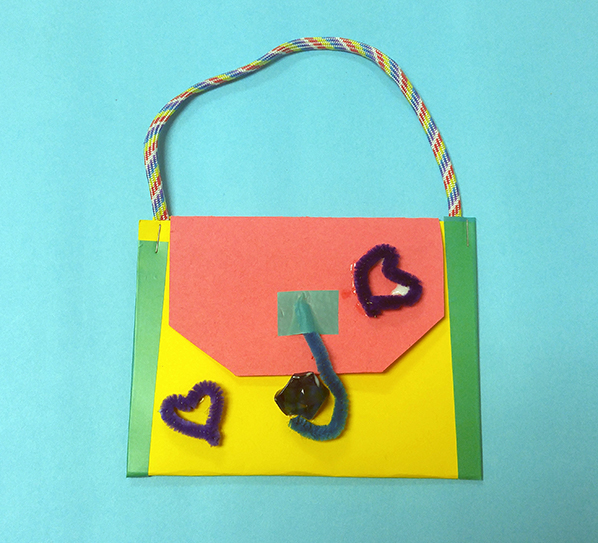
Student exemplar of small pouch created using a variety of fasteners (©2019 Let's Talk Science).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour photograph of a pouch made from paper and yarn.
The pouch looks like a large envelope, with a handle on top, made from thick yarn. Its flap is red paper, the front is yellow, and the edges are green. It is decorated with hearts and a clasp made of black pipe cleaners.
Emotional Awareness
It may not seem like emotions play a big part of STEM, but they do! STEM activities can bring out a range of emotions from confusion and frustration to pride and joy. Teachers should model how to appropriately display these emotions.
Try this!
Computational Thinking activities can be used to make connections to emotions and behaviour. For example, students could use the computational concept of conditionals with phrases about actions and feelings (e.g., if we do not let her join our game then she might feel sad) or the concept of an event as being something that happens based on the input of a user (e.g., input = criticism from a group member, event = walks angrily away).
Critical and Creative Thinking
STEM activities are full of opportunities for critical and creative thinking. This includes things like setting up inquiries and designing and building prototypes to thinking critically and creatively about issues facing the world like climate change.
Allowing students to have some control over what and how STEM learning takes place can give them opportunities to make decisions and solve problems.
Try this!
Help students to develop robust brainstorming skills, using a learning strategy such as carousel brainstorming. Brainstorming is a great way to start design & build activities.
Have students participate in researched-based lessons that allow for multiple viewpoints, such as Should we farm fish and seafood?
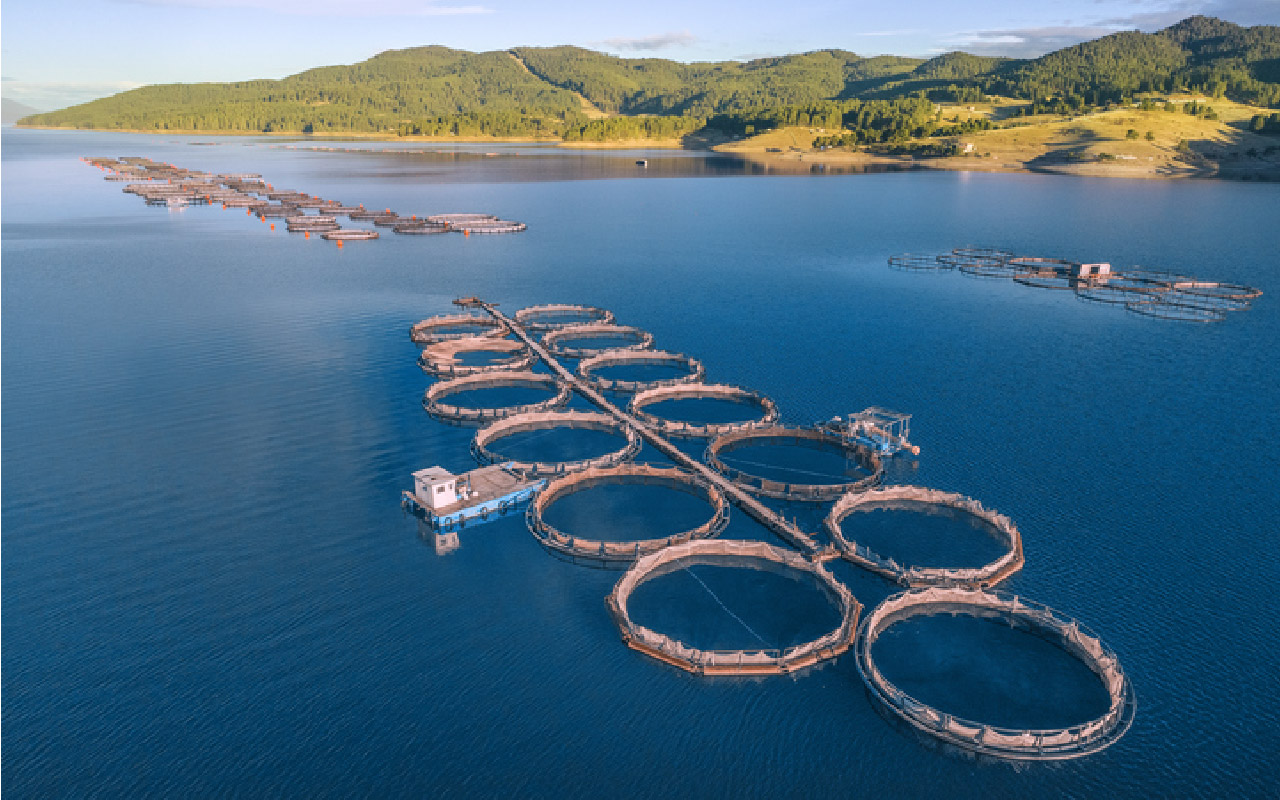

Aerial view of a large fish farm with circular aquaculture pens (Source: Daniel Balakov via iStockphoto).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour photograph of rows of beige hoops, floating on deep blue water.
In the foreground, 13 large hoops are joined to a long stem. A blue platform with a small white hut is attached to the left edge. Another, similar structure floats in the distance. Another smaller group of hoops is to the right, near shore. The land beyond the water is low green hills.
Social Awareness
STEM activities, particularly those involving design thinking, help students to consider the points of view of others ‒ in other words, to show empathy.
Project-based STEM learning that involves having students learn about real-world issues is one way for students to develop empathy while at the same time making a positive impact.
Try this!
Have students participate in projects in which they can see how their individual actions can lead to collective impact, such as Clothing4Climate. In this project, students learn about the environmental impact of the clothing industry, and then take action to make responsible clothing choices.

Screen capture from Clothing4Climate project (©2021 Let’s Talk Science).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour. comic-style illustration of a t-shirt underwater, surrounded by plants.
The short is purple with short sleeves, worn and stained. It floats upright in deep blueish green water. Several different plants grow in, around and through the fabric. The round, blue Clothing 4 Climate logo is in the top left corner.
Healthy Relationships
STEM activities are often collaborative in nature. Such collaborative ventures provide students with the opportunity to develop skills of speaking respectfully, active listening, sharing and making compromises - all skills important to healthy relationships.
In addition to practicing their skills, students should view role models who have used persistence and teamwork to overcome challenges. Role models could be other students, familiar adults and those in STEM professions.
Try this!
Have students learn about famous scientists or inventors who were known for their collaboration, such as:
- Frederick Banting, Charles Best and James Collip
- James Watson and Francis Crick
- Marie and Pierre Curie
- Wilbur and Orville Wright
- William Procter and James Gamble
- Louis Pasteur and Emile Roux
- Joseph-Michel Montgolfier and Jacques-Étienne Montgolfier
Learn More
9 Best Podcasts to Learn More About Social Emotional Learning
How to Approach Social and Emotional Learning in the Classroom
12 Ways to Boost Social-Emotional Learning with STEM