What is Artificial Intelligence?

Chatbot communicating with person (TarkikVision, iStockphoto)

Chatbot communicating with person (TarkikVision, iStockphoto)
How does this align with my curriculum?
| Grade | Course | Topic |
|---|
Learn about the fast-moving field of artificial intelligence and what it means in your life.
To define artificial intelligence, or AI, you need to define what intelligence is. You might think it means being smart. But intelligence is far more than doing well on tests.
Intelligence is complicated. Scientists who study intelligence still have many questions to answer. Are animals intelligent? How are imagination and memory linked to intelligence? Does the size of a brain have anything to do with intelligence?
There are many different definitions of AI out there. Most include the idea that AI is the theory and development of computer systems to do tasks that normally need human intelligence. These include things like recognizing images, interpreting speech, and making decisions.
This backgrounder will help you understand more about AI.
General and Narrow Artificial Intelligence
There are two main kinds of artificial intelligence. These are Artificial General Intelligence and Artificial Narrow Intelligence. It is important to understand the difference between the two.
Artificial General Intelligence
The goal of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is to be equal to human intelligence. Many robotic engineers have managed to create human-like robots. But those robots don’t have intelligence equal to humans yet.
AGI is what you usually see in books and movies that take place in a dystopian future. Some examples of this are the Terminator and the Matrix movies. This is not quite AGI, but superintelligence. Superintelligence is the idea that machines could someday be smarter than humans. But many experts think this is not a threat we should worry about anytime soon.
To develop AGI, scientists look at what we know about human intelligence. They try to understand things like how we learn, or how creativity works. To do this they use things like digital models to copy human behaviours. Brain research can help AI developers. And AGI can help brain researchers understand the brain better!
Artificial Narrow Intelligence
Artificial Narrow intelligence (ANI) is AI we can use right now. Sometimes this is also called weak AI. This lets machines perform actions and make decisions in limited situations. Self-driving cars and virtual assistants are examples of ANI.

Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour illustration of four people using AI tools in a store. Each person is shown in a different part of the store, doing a different task. From left to right, the first person is pushing a shopping cart. Above the cart is a speech bubble with an image of an orange box, an equals sign, and a dollar sign. The same orange boxes are on the shelf behind. This represents a person finding out prices. The second person is carrying a basket. They are using a smartphone to take a photo of a can on a shelf. A speech bubble above their phone shows the can, written information, and a cart icon with a plus sign. This represents a person adding an item to their cart. The third person is carrying a shopping bag. They are holding a smartphone up to a screen with a QR code on it. A speech bubble above the screen shows a credit card and a check mark. This represents a person paying electronically. The fourth person is walking into the store, wearing headphones attached to a smartphone. A speech bubble above their ear shows a musical note and a check mark. This represents a person using a custom playlist.
A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence
The term “artificial intelligence” was first used in 1955. Then, they thought general AI would be possible in a few years. But the technology needed to research AI was not ready.
Here are a few of the milestones in artificial intelligence:
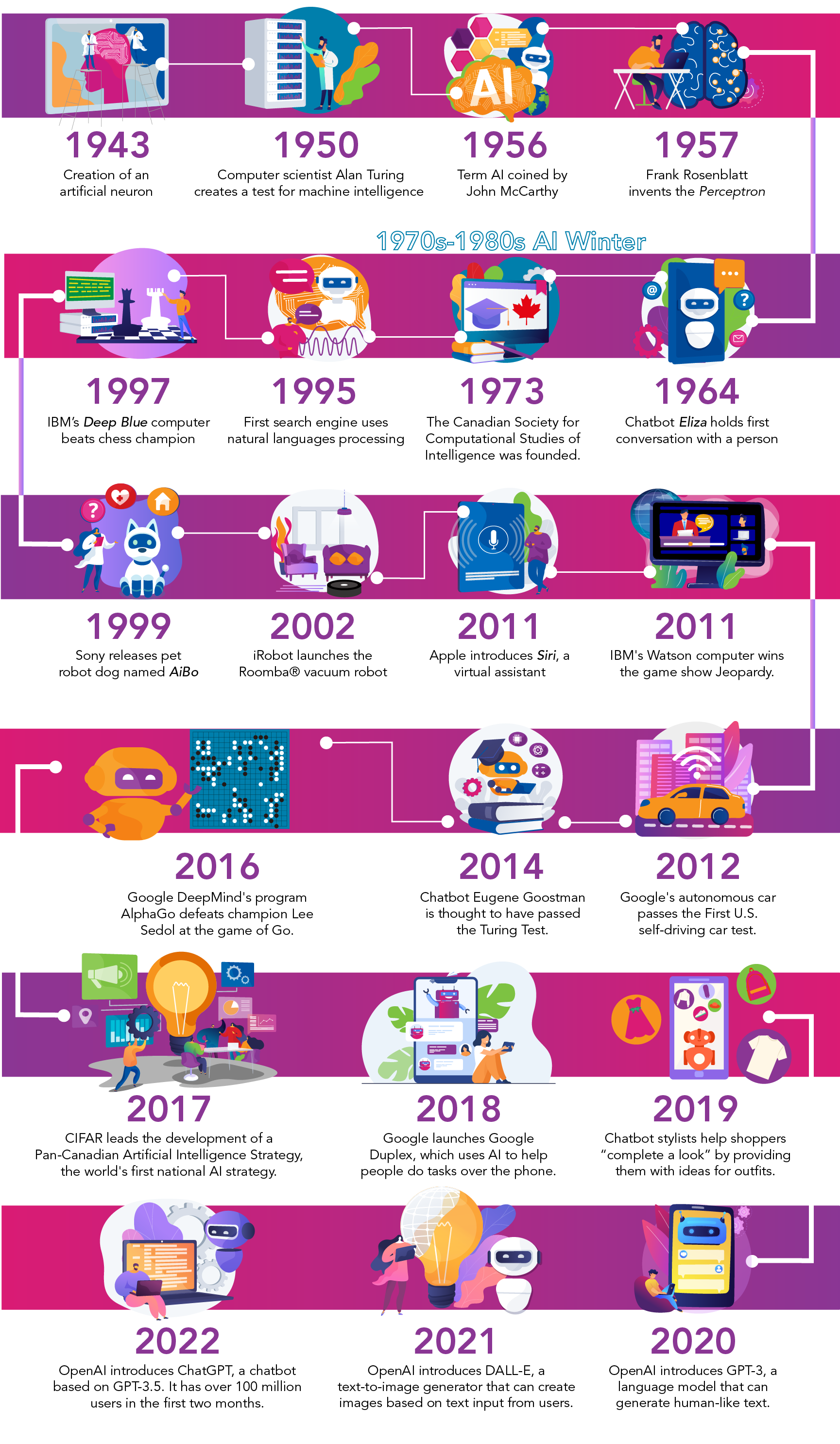
AI timeline (Let’s Talk Science using an image by Visual Generation via iStockphoto)
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour illustration of a timeline from 1943 to 2020.
- 1943: A model for an artificial neuron based on human neurons is created.
- 1950: Computer scientist Alan Turing creates a test for machine intelligence. He called it “the imitation game.” It is now known as the “Turing Test.”
- 1956: The phrase Artificial Intelligence was first published by computer scientists.
- 1957: Frank Rosenblatt invents the perceptron. It is the first computer neural network based on the human brain.
- 1964: The first chatbot, Eliza, holds conversations with humans.
- 1970s-1980s: 'AI Winter', a period where research mostly stopped
- 1973: The Canadian Society for Computational Studies of Intelligence is founded. This is now called the Canadian Artificial Intelligence Association. It is located at Western University.
- 1995: AltaVista is the first search engine to use natural language processing.
- 1997: IBM's Deep Blue is the first computer to beat a chess champion. It defeats Russian grandmaster Garry Kasparov.
- 1999: Sony launches a robot pet dog named AiBO. It’s skills and personality develop over time.
- 2002: iRobot launches the Roomba® floor-vacuuming robot.
- 2011: Apple integrates Siri, an intelligent virtual assistant, into the iPhone 4S
- 2011: IBM's Watson computer wins at the TV game show Jeopardy. This proved it could understand complex human language, because questions included word play.
- 2014: Some experts think computer "chatbot" Eugene Goostman has passed the Turing Test.
- 2014: Google's self-driving car passes the Nevada state self-driving car test.
- 2016: Google DeepMind's program AlphaGo defeats champion Lee Sedol at the game of Go. AlphaGo won four games out of five. At the time, researchers thought this was impossible.
- 2017: Creation of the Pan-Canadian Artificial Intelligence Strategy, a first in the world.
- 2018: Google launches Google Duplex, a service which uses an AI-powered assistant to help people do tasks over the phone.
- 2019: Chatbot stylists help shoppers “complete a look” by providing them with ideas for multiple outfits based on a product. They are also able to recommend alternatives for out-of-stock items.
- 2020: OpenAI introduces GPT-3, a language model that can produce coherent human-like text output.
- 2021: Based on GPT-3, OpenAI introduces DALL-E, a text-to-image generator that can create images based on text input from users.
- 2022: OpenAI introduces ChatGPT, a chatbot based on GPT-3.5. Despite some drawbacks, including its tendency to make things up, it reaches 100 million users within the first two months.
Humans and Computers working together
“Human in the loop” AI is a way to combine the strengths of computers and humans. A computer's strength is its computing speed. Humans will never be able to do calculations as fast as computers. Human strengths include creativity and critical thinking. Humans have the ability to look at a problem from different points of view.
This means humans have many important roles in AI. For example, humans monitor self-driving cars. People responsible for hiring can make sure AI hiring tools are fair. And medical experts can help make sure an AI tool is accurate for all patients.
Artificial Intelligence Opportunities
AI is a great tool. It can help us find solutions to many problems. This is true in any area where we use data, which is almost everywhere!

Image - Text Version
Shown are three colour illustrations of people using AI in different fields. The first illustration represents AI in healthcare. In the image, a person in a white coat holds a tablet and gestures to a large bag of blood in the background. A red tube leads from the bag to a red heart with a white zig zag line across it. Another person, in blue clothes, looks up at the heart from below. The second illustration represents AI in disaster relief. In the image, a person reaches up to catch a box with a white cross on it, falling from the sky with a parachute. There is a pile of similar boxes on the ground. Another person, carrying a red bag with a white cross, is running toward the first. The third illustration represents AI in refugee assistance. In the image, two adults are standing in front of a barbed wire fence. One is holding a small baby. Above, a large, pink, upside-down teardrop icon indicates their location.
In medicine, AI is being used in research. It can help researchers fight cancer or search for vaccines. Some doctors use AI diagnostic tools to help identify illnesses faster. In agriculture, AI can help farmers detect pests and diseases in plants. It can also help to reduce food waste.
AI can also provide tools to help us protect the environment. AI can use satellite images and data to help scientists make predictions. For example, they can use AI to identify where forest fires could happen, before they start. We can also use AI to predict other natural disasters. Scientists can even use AI to understand and protect endangered species. Or protect ecosystems from invasive species.
Did you know?
In 2018, Canadian researchers won the AM Turing Award. This is sometimes called the "Nobel Prize of Computing." This led to the creation of many AI research centres across Canada. And many people now consider Canada an important centre for AI development.
Artificial Intelligence Concerns
Should we be afraid that artificial intelligence might develop beyond human intelligence? Or that it could become a threat to humans? Experts have been debating these issues for a long time. Some people only see AI’s potential for innovation and problem-solving. Others, like Elon Musk and Bill Gates, think AI could be dangerous. They think humans should be very careful about how they develop and use it. That’s why governments are now working to create regulations for AI. These rules will make sure people develop AI applications with human well-being as a priority.
Jobs
AI is already changing the job market. Robots controlled by AI are doing many things that humans used to do. And people are beginning to worry that they will be replaced by machines. During the first industrial revolution, people worried about the same thing.
Some experts predict that AI will make some jobs obsolete. But they also predict it will create more jobs. Some of them call this the fourth industrial revolution. This change will mainly affect jobs that involve manual labour. But it will also affect office jobs where people make routine decisions. These tasks can be automated with AI systems.

Image - Text Version
Shown are three colour illustrations of people using AI to do different tasks. In the first illustration, a person wearing a hardhat and safety vest is watching a machine lift a brick onto a wall. They are holding a tablet. In the background is a large tablet with a blueprint on its screen. In the second illustration, a large robot arm is holding a gear. A person is turning a smaller gear below. In the background, a large tablet displays a document. In the third illustration, a person works on a laptop at a desk. A wifi icon points toward a large robot arm. In the backgrounder are large decorative green leaves and purple gears.
Fairness
AI can solve many problems, but it can also create problems. AI is developing so quickly that some problems are only discovered when a technology is already being used. Like all new technologies, developers can’t always predict how it could go wrong. This is why it’s important for more people to better understand how AI works.
We also need people to follow situations closely when new AI tools are used. This is important because AI is used in more and more areas where it affects people’s lives. These include justice, medicine and banking systems.
For example, the medical data used to train AI needs to represent the characteristics of a whole population. These include things like age, gender and ethnicity. If it does not, then the AI cannot make accurate predictions for that population.
It is important that AI tools don’t create or increase inequalities. Experts are already working on this problem. It is important that people of all backgrounds have access to education in AI. This will help to make sure equity and diversity are better addressed in the future.
In conclusion...
The field of AI is especially important for young people. Its impact on your lives will only increase. But becoming more familiar with AI does not have to mean taking computer science classes. You can learn about it in many different ways. You can start by reading more of our backgrounders on this topic, in the Learn More section.
We may not know exactly what the future holds, but we can be pretty sure that AI will play an important role. And many scientists in Canada are working hard to figure out how humans and machines can build a better world together. Will you join them?
Let’s Talk Science appreciates the contributions of Melissa Valdez Technology Consultant from AI & Quantum for revisions to this backgrounder.
Learn More
What is Machine Learning?
This backgrounder from Let’s Talk Science explains how computers can learn through three different types of machine learning.
AI and Personal Vehicles
This backgrounder from Let’s Talk Science explains how artificial intelligence is integrated into the vehicles that we drive.
AI and Human-Computer Communication
This backgrounder from Let’s Talk Science explains how artificial intelligence and machine learning help us communicate with computers.
AI and Computer Vision
This backgrounder from Let’s Talk Science explains how computers see and learn to recognize objects and human faces.
What The Kids’ Game “Telephone” Taught Microsoft About Biased AI (2017)
This article by Fast Company illustrates the five types of bias that can be found in machine learning applications.
Myths and Facts About Superintelligent AI (2017)
This video from minutephysics (4:13 min.) discusses common misconceptions and true facts about superintelligence.
The Turing test: Can a computer pass for a human? (2016)
This video by TED-Ed (4:42 min.) explains how the Turing Test was used to evaluate if computers have human-equivalent intelligence.
How Snapchat's filters work (2016)
This video by Vox (5:07 min.) explains how visual recognition works, including Snapchat's filters.
References
Chui, M., Chung, R. and van Heteren A. (2019, January 21) Using AI to help achieve Sustainable Development Goals. United Nations Development Program.
Granville, V. (2017, January 2) Difference between Machine Learning, Data Science, AI, Deep Learning, and Statistics. Data Science Central.
Hello Future. How AI can help reduce inequalities (2019)
Leviathan, Y. and Y. Matias (May 8, 2018). Google Duplex: An AI System for Accomplishing Real-World Tasks Over The Phone. Google Research.
Maini, V. (2017, August 19) Machine Learning for Humans. Medium.com
Metz, C. (Nov 24, 2020). Meet GPT-3. It Has Learned to Code (and Blog and Argue). The New York Times.
O'Brien, M. (Aug. 1, 2023) Chatbots sometimes make things up. Is AI's hallucination problem fixable? Associated Press.
OpenAI (n.d.). DALL-E: Creating images from text.
Stark, L. and Zenon W. Pylyshyn. (2020, March 10). Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Canada. The Canadian Encyclopedia.
Sample, I. (Oct 30, 2019). AI becomes grandmaster in 'fiendishly complex' StarCraft II. The Guardian.
Timelines Wiki. Timeline of machine learning. (2020).
Wingate, J. (2018, April 30) Why Artificial Intelligence Will Make You Question Everything.