Innovations in Nuclear Technologies
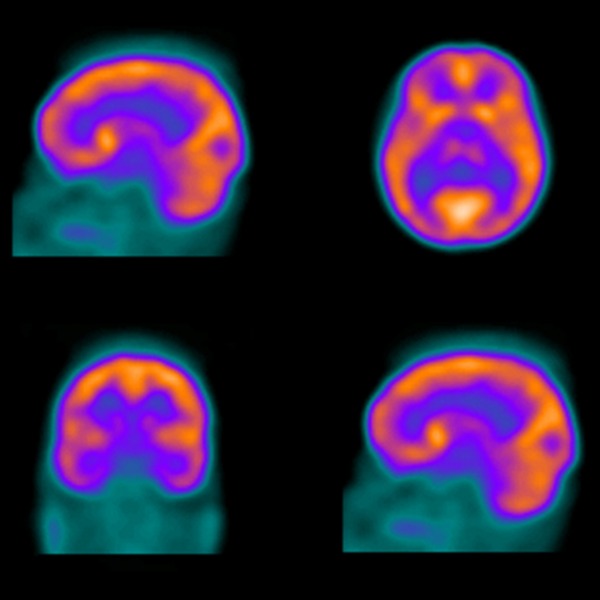
Medical image of the brain using Technetium-99m (wenht, iStockphoto)

Medical image of the brain using Technetium-99m (wenht, iStockphoto)
8.2
How does this align with my curriculum?
Curriculum Alignment


