Introduction to Climate Change

Our climate is changing (filo, iStockphoto)

Our climate is changing (filo, iStockphoto)
How does this align with my curriculum?
Learn more about the causes and impacts of global climate change.
What is climate change?
Climate change is a change in the usual weather patterns in a region over time. Temperatures on Earth have been rising dramatically for many years. This change is impacting local climates all around the world.
Changes in weather happen all the time. But weather and climate are not the same thing. Weather is the day to day change in temperature and precipitation in a place. You can describe the weather in your community by looking outside. If it’s cold and snowy right now, that’s today’s weather.
Climate, on the other hand, is the usual weather in a place over a long period of time. Weather can change quickly. It might be sunny in the morning and rainy in the afternoon. Climate changes much more slowly. Until recently, Earth’s climate had been about the same for 9000 years.
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour illustration of a set of clothes for one day, labelled “Weather,” and a closet full of clothes, labelled “Climate.” On the top left of the image is the title “Weather” in black letters. Below, a subtitle reads “What you wear each day.” Below, several items of clothing and a yellow sun are against a green background. These include a baseball cap, sunglasses, t-shirt, shorts, and flip flops. On the top right of the image is the title "Climate" in black letters. Below, a subtitle reads“What you wear over the year”. Below is a wardrobe with both doors open. Inside, clothes are hanging on the doors and piled on shelves. These include jackets, jeans, sweaters, a vest, t-shirts, scarves, toques and mittens. On the floor in front are winter boots, running shoes, brown shoes and an umbrella.
How do we know the world’s climate is changing?
The world’s average temperature has changed throughout history. Sometimes the world’s temperature has been warmer and sometimes it has been colder. Factors like ocean currents and volcanic eruptions caused these shifts. They are part of a natural cycle of heating and cooling. This usually happens over tens of thousands of years.
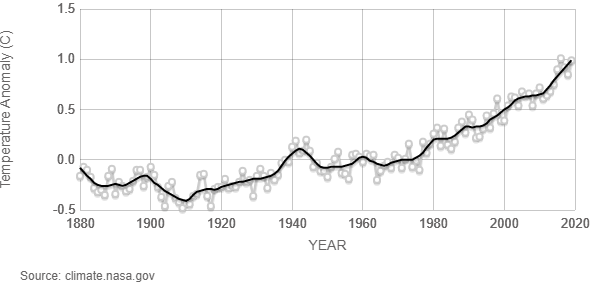
Image - Text Version
Shown is a black and white graph that shows the change in global surface temperature compared to the long-term average. The y axis is labelled “Temperature Anomaly (C)". It runs from -0.5 to 1.5. The x axis is labelled “Year.” It runs from 1880 to 2020. A wavy, black horizontal line shows an overview of the temperature anomaly through the years. Small grey dots are shown above and below this, representing specific anomalies. Between 1880 and 1980, the line dips just above and below 0.0 degrees Celsius. From 1980 to 2020, the line slopes up, reaching 1 degree Celsius.
But now Earth’s climate is changing faster than it ever has during human history. Earth’s average temperature has increased by at least 1.1 °C since 1880. And most of that warming has happened since 1975. In fact, 2023 will probably be the warmest year ever recorded.
This trend of rising global temperatures is called Global warming. Global warming is one of the ways that Earth’s climate is changing. Climate change also involves changing global weather patterns, ocean currents, and other systems.
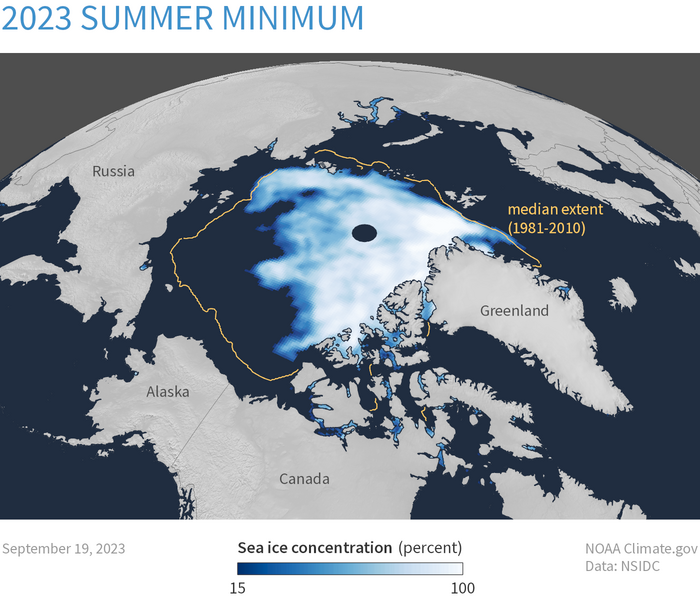
We are already experiencing these changes. Scientists have observed rising sea levels, melting ice and increasing extreme weather events. These changes affect each region differently. For example, snow and ice are melting so quickly that the Arctic could have no summer sea ice by 2030. Coastal areas are experiencing more flooding. These are all evidence of climate change.
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour illustration of an area of ice around Earth’s north pole, with a line showing a larger area between 1981 and 2010. Near the centre of the image is a dark blue sunburst representing the north pole. It is surrounded by an uneven blob of cloudy white. The edges of this area fade into the dark blue that represents water. The ice extends to northern Canada and Greenland, but does not touch Russia or Europe. Outside this area, a wavy yellow line in the water is labelled “median extent 1981-2010.” This extends much further, touching northern Russia, coming close to Alaska, and halfway down the coast of Greenland.
Why is the climate changing?
These changes to Earth’s climate are not natural shifts. Scientists are confident that human activities are the leading cause of climate change. Human activities release gases that change Earth’s atmosphere. These gases are making our atmosphere better at trapping the Sun's heat. We call this the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect is the main cause of rising temperatures on Earth.
So what is the greenhouse effect? Plants can grow better in a greenhouse because it stays warmer than the outside air. This is because heat from the Sun enters through clear glass or plastic, then gets trapped inside. This heat keeps the greenhouse warm.
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour illustration of sunbeams shining into a glass greenhouse, where they are trapped. The beams are long yellow arrows that stretch diagonally down from the Sun at the top left of the image. They go through the roof and walls of the greenhouse. There, they bounce up from the plants on the ground, and stop when they hit the roof above. Outside the greenhouse, the ground is covered in snow. To the left, a snowman has a worried expression.
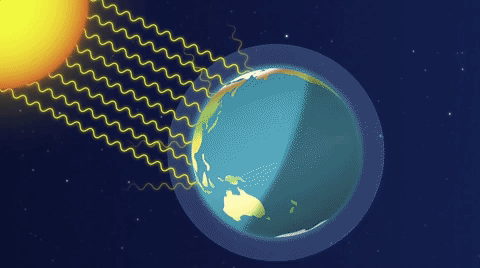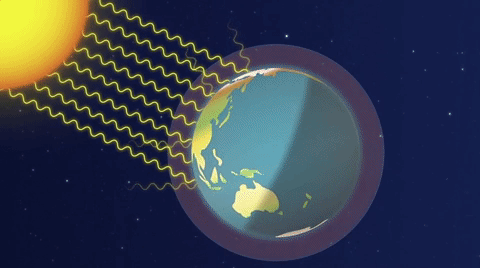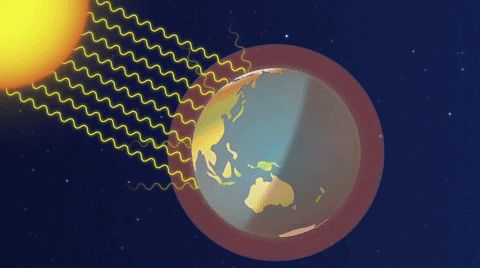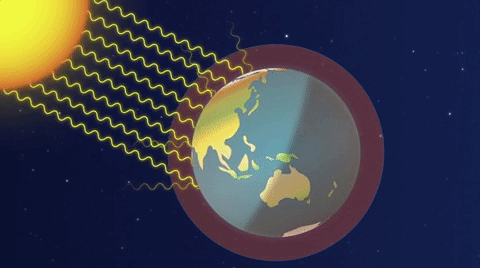
A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect (Source: ESA).
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour animation illustrating how heat from sunlight is trapped in Earth’s atmosphere. The title “The Greenhouse Effect” is in bold letters at the top right. Earth is shown as a half circle at the bottom of the screen. There is a thick stripe of misty, pale blue above the surface. A blue line along the top of this area is labelled “Atmosphere.” The Sun is shown as a glowing white circle in the top left corner. First, curved white lines radiate down from the sun, through space to the surface of Earth. Text appears reading “Sunlight reaches the Earth.” Next, smaller, fainter curved lines radiate from Earth, up into space. Text appears reading “Some energy is reflected back to space.” Then, text appears reading “Some is absorbed and re-radiated as heat.” Earth’s atmosphere begins to turn from blue to pink. Finally, bursts of bright orange arrows appear in the atmosphere. Text appears reading “Most of the heat is reflected by greenhouse gases and then radiated in all directions, warming the Earth.”
The greenhouse gases in our atmosphere help keep our planet warm enough for us to survive. Too little greenhouse gas would make Earth too cold for humans. But, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm. Over the past century, humans have added a lot of greenhouse gases to our atmosphere.
Did you know?
The average temperature on Earth would be -18°C without the greenhouse effect.
Carbon dioxide is the most common greenhouse gas in our atmosphere. Carbon moves between the Earth, living things, and the atmosphere in the carbon cycle. Like all animals, humans add carbon dioxide to the atmosphere when we breathe. We also emit a lot more carbon dioxide when we burn fossil fuels. These are fuels we dig up like oil, gas and coal which are made of plant and animal remains from millions of years ago. We burn fossil fuels when we drive cars, heat our homes, and generate electricity. Humans have burned large amounts of fossil fuels over the last century.
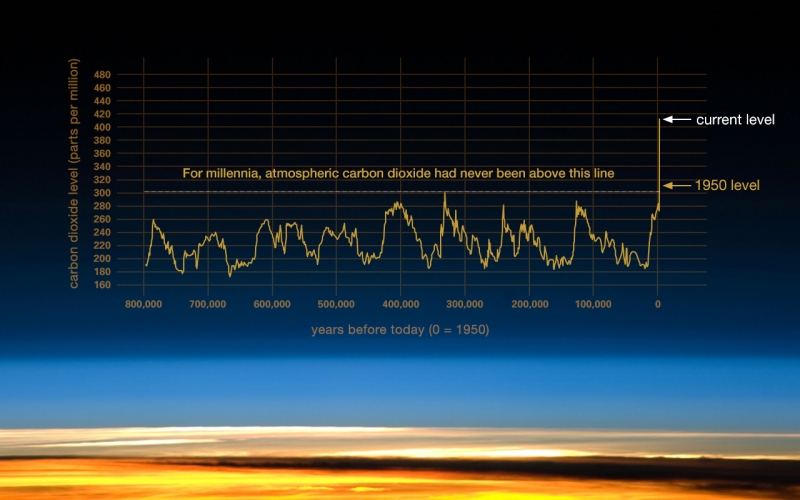
The amount of carbon dioxide in the air is now nearly 50% more than in 1750. About 25% of that change has happened since 2000. Carbon dioxide concentrations haven’t been so high for over three million years.
Image - Text Version
Shown is a line graph overlaid on a colour photograph of Earth’s atmosphere. The x axis is labelled “years before today (0 = 1950).” This runs from 800,000 on the left to 0 on the right. The y axis is labelled “carbon dioxide levels (parts per million).” This runs from 160 at the bottom to 480 at the top. A horizontal, dotted line crosses the whole graph at 300 ppm. This is labelled “For millennia, carbon dioxide had never been above this line.” Below, the jagged line representing carbon dioxide levels zig-zags up and down 800, 000 years before today to almost 0. Just before 0, the line shoots up past 300 ppm, becoming completely vertical. Just over 300 ppm, this is labelled “1950 level.” The top of this, about 420 ppm, is labelled “current level.” The photograph in the background shows streaks of colour indicating sun and clouds at Earth’s surface, and blue sky darkening into black space.
Methane (CH4) is the next most common greenhouse gas. Methane has about 80 times the warming power of carbon dioxide. This makes methane an important gas to keep an eye on. The main sources of methane in Canada are from fossil fuels use, farming, and waste.
What are the impacts of climate change?
Increasing the global temperature by a few degrees may not seem that bad. This is especially true if you live in a relatively cold country like Canada. But, think about how you feel when you have a fever. Raising your body temperature by just a couple degrees can make you feel terrible. Like our bodies, Earth is a series of intertwined systems. Rising global temperatures have complex and sometimes unexpected impacts that affect us all. These can already be felt in Canada and around the world.
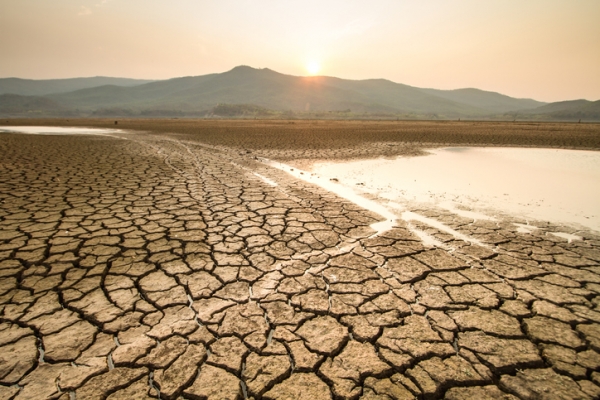
The impacts of climate change are complex. And they are different for every region. In some places, higher temperatures have already led to megadroughts and heat waves. They are also causing extreme rain and snowstorms in some places. Climate change could continue causing melting sea ice, glaciers, warming oceans, and rising sea levels. These changes impact people, plants, and animals.
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour photograph of dry, cracked mud with puddles of water. The camera is focused on a light brown, nearly flat surface in the foreground. Here, mud has dried forming deep, jagged cracks. On the right and left, wide, shallow puddles of brown water gleam in the sun. In the background, the Sun peeks out over low, hazy, blue green mountains.
Additionally, climate change will continue to affect our planet for many years. Carbon dioxide stays in the atmosphere for hundreds of years. It can take some time for Earth's complex systems to respond to changes.
How can we tackle this problem?
Our response will determine how much our climate will change. There are two main ways to deal with climate change. These are adaptation and mitigation. Adaptation is about finding ways to cope with our changing climate. For example, cities could adapt to rising sea levels by building walls or using pumps to prevent flooding.
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour photograph of a pile of sandbags on a street filled with water. The camera is focused on a concrete barrier in the foreground. It is covered in a sheet of plastic and topped with small cinched white bags filled with a heavy material. In the background, a street is filled with water. A row of houses on the right is blocked off with yellow caution tape.
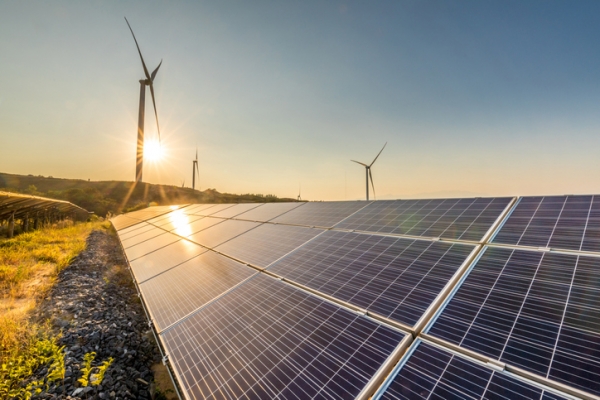
Mitigation is about finding ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. For example, we could burn less fossil fuel by using cars and other gas-powered vehicles less. We can also use solar or wind power, instead of fossil fuels, to generate electricity. These changes need work and cooperation from people around the world.
Image - Text Version
Shown is a colour photograph of three wind turbines and two rows of solar panels. The camera is focused on the blue, gridded panels in the foreground. The backs of another row of panels is visible to the left. Both rows stretch toward the horizon. The Sun is close to the horizon and its light is reflecting off the panels. The wind turbines are in the background, silhouetted against blue and gold sky.
Climate change is a difficult issue to solve because of its global scale and complexity. Luckily, many people are concerned about climate change. Young people in particular are encouraging governments and businesses to take action. Many organizations are trying to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Government plans, international agreements, and emerging technologies will all need to play a role. There is a lot of work and research that still needs to be done. But we humans are up for it!
Learn More
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
Learn more about the greenhouse effect with this hands-on activity from Let’s Talk Science.
Timelapse - Warming Planet (2023)
See how Earth has changed since 1987 with images of melting ice and glaciers, shrinking lakes, increasing fires, and extreme weather.
What is Climate Change?
Learn more about climate change from NASA Kids.
Why Does Climate Change Matter NASA Earth Minute: Usual Suspects (2023)
This video (1:34 min.) from NASA explains how we are already feeling the effects of climate change, and how scientists are helping us understand and prepare for it.
Climate 101 with Bill Nye (2012)
Learn about the basics of climate change in this video (4:33 min.) with Bill Nye.
References
Climate Reality Project. (November 7, 2019). Climate Adaptation vs.Mitigation: What’s the Difference and Why Does it Matter?
NASA. (n.d.). Global Climate Change.
NASA. (n.d.). How do we know the climate is changing?
NASA. (n.d.). What is the greenhouse effect?
NOAA. (August 7, 2020). Climate is what you expect, weather is what you get
Oss Foundation. (2014). Milankovitch Cycles.